Describe the Structure and Function of Dna and Rna
A DNA nucleotide contains deoxyribose sugar whereas an RNA contains the sugar ribose in every nucleotide. RNA is typically single stranded and is made of ribonucleotides that are linked by phosphodiester bonds.

Dna Rna New Classroom Biology Science Poster Science Biology Biology Poster Teaching Biology
The DNA structure defines the basic genetic makeup of our body.

. Please provide an example of how structure relates to function in DNA or in RNA. -composed of polynucleotides -- have a phosphate group deoxyribose sugar and a nitrogen containing bases adenine thymine cytosine and guanine -Has a doubled helix that is formed by hydrogen bonds between polynucleotides. DNA contains thymine T whereas RNA contains uracil U.
Replicates and stores genetic information like a blueprint. The main function of RNA is to carry information of amino acid sequence from the genes to where proteins are assembled on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA tRNA What does messager RNA do.
Apart from this DNA has a double helix in its structure that is RNA is a. DNA is written in linear strands of nucleotide. Or describe another way genes are regulated.
DNA and RNA contain the same purines namely adenine A and guanine G. Nucleic acids are macromolecules or biopolymers. DNA and RNA are involved in the synthesis of proteins.
RNA is also referred to. -Densely compacted into chromosomes to fit into nucleus. The most commonly occurring purines in DNA are adenine and guanine.
The monomers of these nucleic acid compounds are nucleotides. Transcription is the transfer of info from DNA to RNA. RNA resembles the same as that of DNA the only difference being that it has a single strand unlike the DNA which has two strands and it consists of an only single ribose sugar molecule in it.
This nucleic acid is responsible for the production of new cells in the human body. This completes their respective names. -mRNA is produced in the nucleus by transcription using DNA as a template -contains bases complimentary to DNA -Carries DNAs message out of the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
Proteins within a cell have many functions including building cellular structures and serving as enzyme catalysts for cellular chemical reactions that give cells their specific characteristics. Nucleic acids are the organic materials present in all organisms in the form of DNA or RNA. Biologists in the 1940s had difficulty in accepting DNA as the genetic material because of the apparent simplicity of its chemistry.
They are comprised of nucleotide chains linked via. DNA was known to be a long polymer composed of only four types of subunits which resemble one another chemically. In DNA this is deoxyribose while in RNA its ribose.
These nucleic acids are formed by the combination of nitrogenous bases sugar molecules and the phosphate groups that are linked by different bonds in a series of sequences. DNA and RNA are found to be very important constituents in the living cell. STRUCTURE OF DNA.
As has been said RNA has a different nitrogen base uracil than thymine and is composed of a different sugar than deoxyribose ribose. DNA is the usual genetic material of the most organisms while RNA is the genetic material of some viruses. Both DNA and RNA have specific languages.
The genes in DNA contain the instructions for the amino acid sequence of a protein. Both DNA and RNA are made from nucleotides each containing a five-carbon sugar backbone a phosphate group and a nitrogen base. The difference between RNA and DNA is based first of all on their constitution.
Translation is the transfer from RNA to proteins. Unlike DNA RNA contains a uracil nitrogenous base instead of thymine. Most of the DNA is found in the chromosomes.
If an enzyme is defective then the cell may not be able to perform a chemical reaction. The key difference between DNA and RNA structure is that the DNA structure is a double helix composed of two complementary strands while RNA structure is single-stranded. Length DNA is a much longer polymer than RNA.
The most commonly occurring pyrimidines in DNA are cytosine and thymine. The function of a gene is to dictate the production of a polypeptide. Whereas the RNA is formed in the chromosomes and occur in.
There are many possibilities there. Messanger RNA mRNA 2. The structures of major purines and pyrimidines found in nucleic acids are shown in Fig.
Describe operons and their contribution to homeostasis. However whereas DNA molecules are typically long and double stranded RNA molecules are much shorter and are typically single stranded. They are both linear polymers consisting of sugars phosphates and bases but there are some key differences which separate the two 1.
RNA is a smaller and more complex molecule than DNA. What are the 3 different functions of RNA. Although both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids there are key differences in the structure and function of RNA and DNA.
Hence is the name Ribonucleic acid. RNA programs protein synthesis with two phases. However the nucleic acids differ with respect to the second pyrimidine base.
Type of sugar The backbones of both DNA and RNA are a sugar molecule and a phosphate group. RNA molecules perform a variety of roles in the cell but are mainly involved in the process of protein synthesis translation and its regulation. Cells access the information stored in DNA by creating RNA to direct the synthesis of proteins through the process of translation.
Since enzymes are proteins an error in the gene for that enzyme could render the enzyme non-functional. Deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid. Structurally speaking ribonucleic acid RNA is quite similar to DNA.
Function of rna and dna. In protein synthesis the area of bases required to code for a protein is unzipped the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases are broken down by the enzyme helicase and. The subtle structural difference between the sugars gives DNA added stability making DNA more suitable for.
Further the pyrimidine cytosine C is found in both DNA and RNA. Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA are perhaps the most important molecules in cell biology responsible for the storage and reading of genetic information that underpins all life. Ribosomal RNA rRNA 3.
They are also found in the cytoplasm as in mitochondria and chloroplast. DNA provides the code for the cell s activities while RNA converts that code into proteins to carry out cellular functions. Early in the 1950s DNA was first examined by x-ray diffraction analysis a technique for determining the three-dimensional.
The function of DNA is to hold or store genetic information DNA is the molecule that contains the instructions for the growth and development of all organisms RNA The function of RNA is to transfer the genetic code found in DNA out of the nucleus and carry it. It is usually obtained from the DNA molecule. The purines and pyrimidines.
Moreover they are the building blocks of genetic material of an organism. RNA Structure and Function. In basic terms DNA contains the complete genetic code of an organism whereas RNA contains a small amount of transcripted DNA that is used for a specific function for instance making proteins.
There are three types of RNA and each is involved in protein synthesis. The nitrogenous bases in DNA can be adenine guanine cytosine and thymine. Ribonucleic acid RNA also consists of nucleotides but these nucleotides contain the sugar ribose.
Provide an example of polygenic inheritance of a trait in plants or animals including humans of course. They also contain a sugar group of a 5-carbon ring called a pentose. DNA deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA ribonucleic acid are composed of two different classes of nitrogen-containing bases.
Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids thats the NA part of their acronym. RNA and DNA. The sequence of nitrogen bases A T C G in DNA is what forms an organisms traits.
A ribonucleotide in the RNA chain contains ribose the pentose sugar one of the four nitrogenous bases A U G and C and a phosphate group. RNA has ACG and U.

Difference Between Dna And Rna Comparison Summary Study Biology Biology Facts Biology Notes
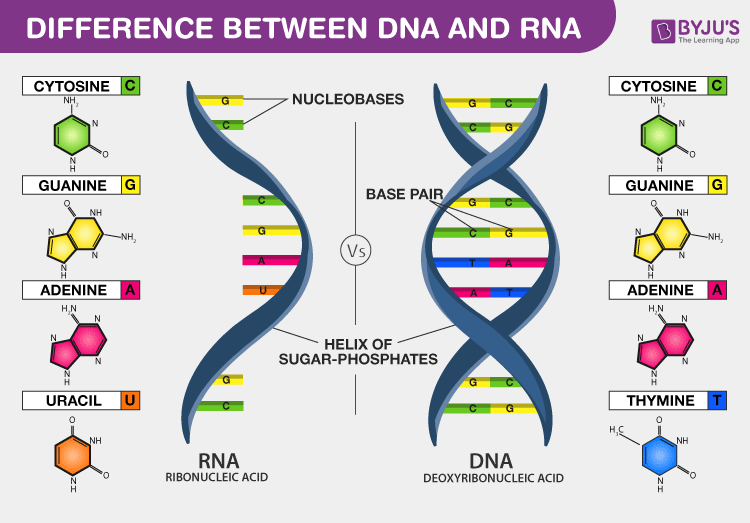
Dna Vs Rna Introduction And Differences Between Dna And Rna

Structure Of Dna Biology Worksheet Dna Worksheet Dna Lesson Plans

Dna Structure Function Homework Worksheet Homework Worksheets Persuasive Writing Prompts Worksheets

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks

Pin On The Ingredients Of Life

Steps Of Dna Replication Dna Polymerase Dna Replication Biology Lessons

Structural Differences Between Rna And Dna Coloring Page Free Printable Coloring Pages Color Worksheets Dna Worksheet Dna Drawing

Dna Vs Rna Vector Illustration Vectormine Biology Lessons Biology Classroom Study Biology

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks

Do You Know The Differences Between Dna And Rna Biology Notes Study Biology Teaching Biology
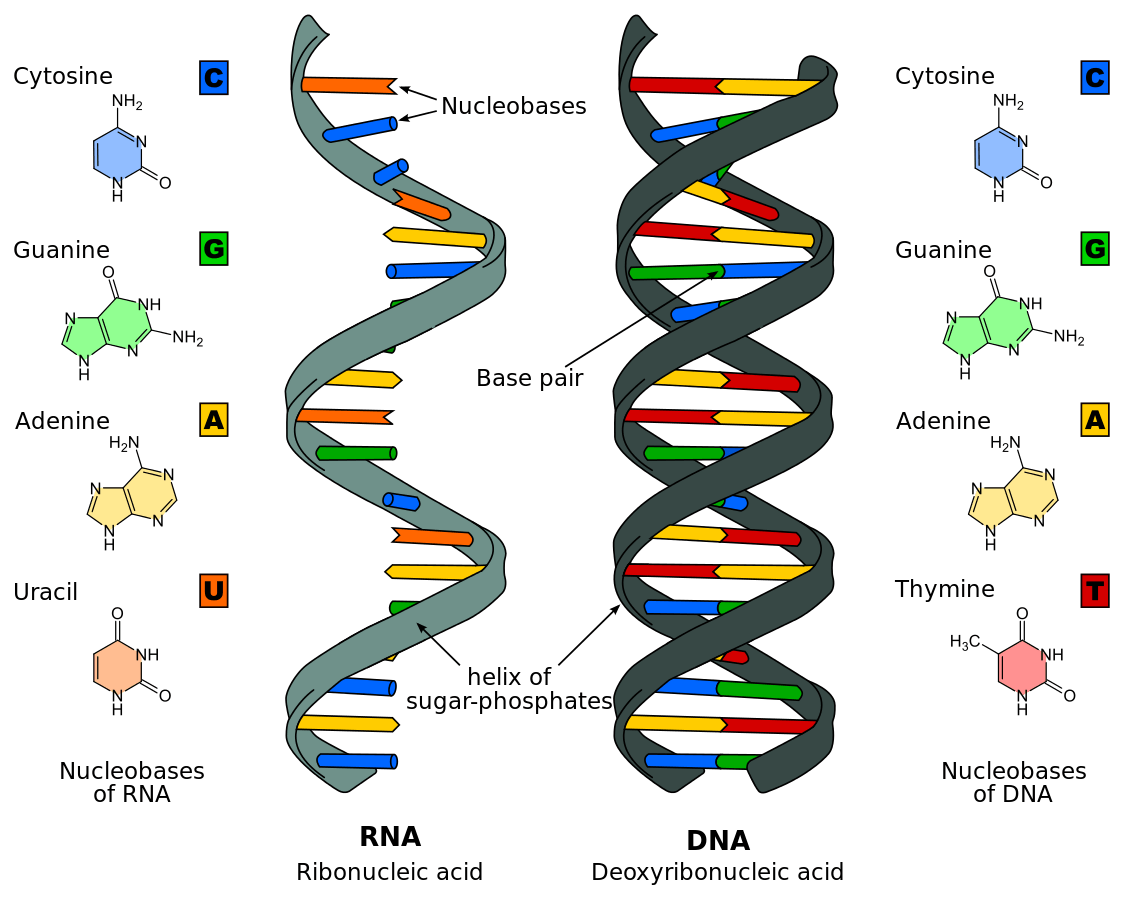
Dna And Rna Structure Function Expii

Dna Rna Adn Y Arn Molecula De Adn Maqueta Molecula Del Adn






Comments
Post a Comment